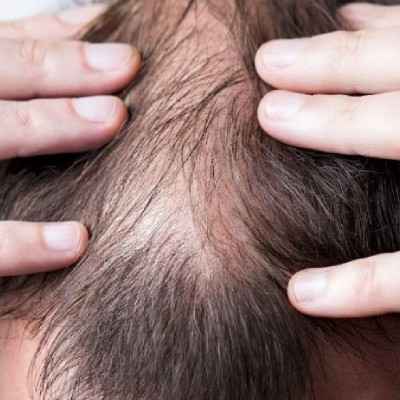
Understanding Autoimmune-Related Hair Loss and Treatment Options

10 July 2024
drgarg

In autoimmune disorders, the immune system wrongly targets the body's healthy cells and tissues for destruction. Normal cells can occasionally be mistaken for foreign by the immune system, which normally works to defend the body from invaders like viruses and bacteria. Skin, joints, and the neurological system are just a few of the body's organs and systems that autoimmune illnesses can impact.
Common Autoimmune Diseases that Cause Hair Loss
An autoimmune condition is one of the most frequent causes of hair loss, especially when it starts before age 50. Hair loss is one of the most known side effects of these disorders, along with other symptoms. Here are some of the most prevalent autoimmune diseases that result in hair loss.- Alopecia Areata An autoimmune condition known as alopecia areata harms the hair follicles and causes tiny, circular bald patches on the scalp. Additionally, it can show an impact on the beard and eyebrows. Alopecia totalis or alopecia universalis, which are extreme forms of the condition, can result in total hair loss on the head or the entire body.
- Lupus The autoimmune disease lupus may impact the skin, joints, kidneys, blood vessels, and other bodily components. Lupus patients frequently have hair loss, which can take the form of patches or be more pervasive. Additionally, thin, weak, and easily broken hair is possible.
- Chronic Hashimoto's Thyroiditis An autoimmune condition known as Hashimoto's thyroiditis damages and inflames the thyroid gland. This disorder frequently manifests as scattered or patchy hair loss. Fatigue, weight gain, and a sensitivity to the cold are further signs of Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
- Graves Disease Another condition that causes hair fall due to thyroid is this one. In Graves' disease, antibodies attach to the thyroid cells' surface, encouraging them to overproduce thyroid hormones and causing hyperthyroidism, hair loss, or an overactive thyroid. It may also impact where new hair is produced on the body and scalp. You can treat Graves' disease with anti-thyroid medications such as propylthiouracil and methimazole, which prevent thyroid hormone generation. You must always consult with a hair expert and let them analyze the condition and suggest the best course of action.
How do Autoimmune Diseases Lead to Hair Loss?
In autoimmune disorders, the immune system targets the body's healthy cells and tissues for destruction. Hair follicles typically undergo three phases: growth, rest, and shedding. But in autoimmune hair loss, the immune system harms the hair follicles, causing premature hair loss.- Uncertainty exists regarding the precise mechanisms underlying autoimmune-related hair loss. T-cells become activated and harm the body's healthy tissues by attacking hair follicles and interfering with the regular hair development cycle.
- According to researchers, autoimmune-related hair loss may be caused by genetic and environmental causes. According to some studies, certain genes may raise the likelihood of having autoimmune disorders, including those that impact hair development. Environmental factors like stress, infections, and hormonal changes may also trigger or worsen autoimmune-related hair loss.
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune illness that can result in hair loss. The immune system destroys hair follicles in alopecia areata, resulting in hair loss in tiny circular patches on the scalp. Hair loss is a frequent sign of lupus, an autoimmune illness that affects the thyroid gland.
- Not all cases of hair loss are brought on by autoimmune illnesses, and it is crucial to remember this. Age, genetics, hormonal changes, and some medications are additional factors that might cause hair loss. One can determine the best solution if the cause of hair loss is ascertained with a comprehensive examination by a hair doctor specializing in hair loss.
Treatment Options for Autoimmune-Related Hair Loss
Although no known hair loss treatment for autoimmune-related hair loss exists, some approaches can help control the
signs and encourage hair regrowth. The underlying autoimmune illness and the degree of hair loss determine the
treatment method.
- Hair Transplant Hair transplants are common for patients with severe hair loss, where hair follicles are extracted from a donor area of the head and transplanted to bald or thinning areas. However, in case of an autoimmune disease, the body is already at a vulnerable stage, so opting for a hair transplant becomes a far-fetched reality and a path where one should not tread without medical guidance. Hair transplants for autoimmune disease cases should be reviewed with a healthcare professional only since it’s uncertain what reaction the treatment can trigger.
- Hair Extension A non-surgical technique to lengthen and volumize hair is hair extensions. They are available in many hues and textures and can be constructed of genuine or synthetic hair. They are only short-term fixes that need care and will eventually be replaced.
- Laser Therapy Low-level laser light is used in laser therapy to promote hair regrowth. You can use a portable laser device for the therapy at home, or a more potent laser can be used in a hospital setting. It is a non-invasive procedure with few known adverse effects. Before beginning treatment, you should discuss laser therapy with a medical professional.
When should I see a Hair Specialist Doctor?
It's crucial to visit a hair specialist doctor who focuses on hair loss if you're experiencing hair loss. They can comprehensively evaluate and identify the underlying reason for your hair loss. If an autoimmune disease is found, we advise you to seek hair loss therapy from a doctor specializing in such conditions. If you have an autoimmune disorder causing hair loss, working closely with your medical team will help you manage your symptoms and halt further hair loss. They can guide you with the best course of action for your circumstances and track your development.Conclusion
In conclusion, hair loss caused by autoimmune conditions can be a troubling sign of many autoimmune disorders. There are, however, therapeutic alternatives that can support hair restoration while managing symptoms. If you detect hair loss, you must see a hair doctor at the AHS hair clinic to get a correct diagnosis and treatment. By offering excellent hair treatments and consultations, AHS gives the best course of action and desired results. Make an appointment at the local AHS hair clinic to get your desired hair.Stay Updated
Subscribe to our email newsletter for helpful tips and valuable resourses
Be an influencer
Join forces with Advanced Hair Studio! Explore exciting collaboration opportunities tailored for influencers. Let's redefine haircare together.
Connect now